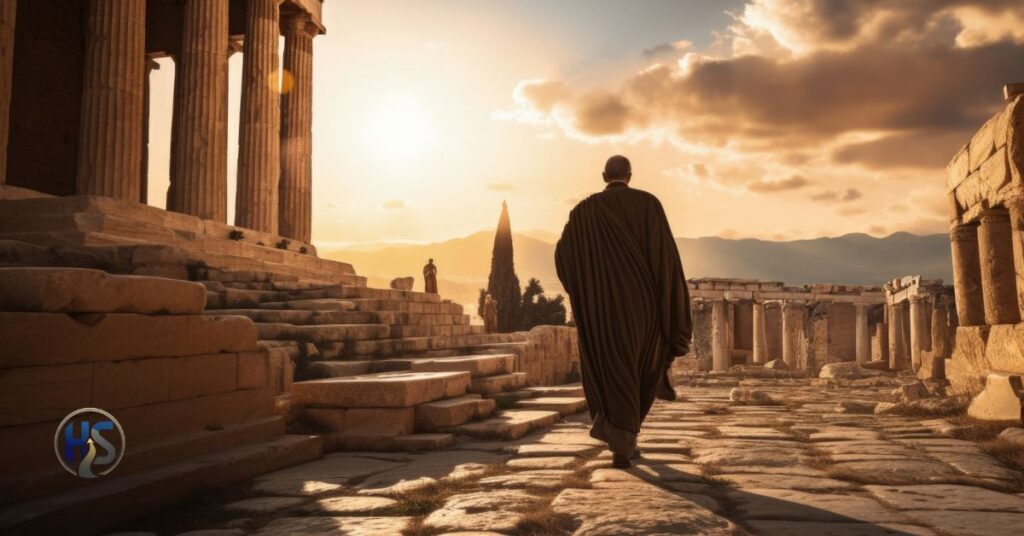
Civilizations rise on ideas, armies, and ambition, but they endure on infrastructure. The Cesta Roman, the Roman road system, was not just stone laid on soil. It was a calculated instrument of control, commerce, culture, and continuity. While empires before Rome built roads, none built them with such precision, scale, or foresight. These routes did not merely connect cities; they synchronized an empire.
To understand Rome’s longevity, military dominance, and cultural reach, you must understand its roads.
What “Cesta Roman” Really Means
At its core, Cesta Roman translates to Roman road. Linguistically, “cesta” denotes a path or constructed way, while “Roman” anchors it firmly within the framework of Roman statecraft and engineering philosophy.
But treating Cesta Roman as a simple translation undersells its significance. In Roman thinking, a road was never neutral. Every mile carried authority. Every stone announced permanence. These roads were built to last, and many of them still do.
The Scale: Numbers That Still Shock Engineers
Rome did not experiment with roads. It industrialized them.
- Over 400,000 kilometers of total road network
- Approximately 80,000 kilometers paved with stone
- Roads spanning three continents: Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia
- Major routes still visible or directly reused in modern highways
This was not accidental growth. It was centralized planning executed over centuries with ruthless consistency.
Roman Road Engineering: Brutally Practical, Quietly Brilliant
Roman roads succeeded because they ignored shortcuts and punished laziness.
Layered Construction That Defied Time
A standard Cesta Roman road followed a disciplined structure:
- Statumen—large foundation stones
- Rudus—compacted rubble mixed with lime
- Nucleus—fine gravel or sand
- Summum dorsum—tightly fitted paving stones
This design delivered:
- Load distribution for heavy military traffic
- Natural drainage through cambering
- Resistance to erosion and freeze-thaw cycles
Modern civil engineers still study these cross-sections—not out of nostalgia, but respect.
Surveying Without Guesswork
Roman surveyors used tools such as the groma and chorobates to achieve astonishing straightness. When obstacles appeared, they didn’t bend the road. They cut through hills, bridged valleys, and drained swamps.
Efficiency mattered. Symbolism mattered more.
Why Rome Built Roads: Power Moves in Stone
Cesta Roman served four strategic purposes, each reinforcing the others.
Military Supremacy
Roman legions could march up to 30 kilometers a day on paved roads—twice the speed of many adversaries. This allowed Rome to:
- Deploy forces rapidly
- Suppress revolts before they spread
- Maintain supply lines deep into frontier territories
The road arrived before rebellion, and rebellion rarely survived it.
Economic Integration
Merchants moved grain, wine, olive oil, metals, and textiles with unprecedented predictability. Standardized roads reduced:
- Transport costs
- Transit time
- Risk of spoilage
Markets expanded. Regional economies fused. Rome taxed all of it.
Administrative Control
Couriers using the cursus publicus (state communication system) could carry official messages across provinces in days, not weeks. Governors ruled from afar because roads collapsed distance.
Paperwork travels faster when stone leads the way.
Cultural Transmission
Language, law, architecture, and religion—none spread in isolation. Roads enabled:
- The diffusion of Latin
- The spread of Roman legal systems
- Urbanization based on Roman city grids
- Eventually, the rapid expansion of Christianity
Cesta Roman didn’t just move people. It moved ideas.
Iconic Roman Roads That Shaped History
Via Appia—The Queen of Roads
Built in 312 BCE, the Via Appia connected Rome to southern Italy. It featured:
- Precision paving
- Monumental tombs
- Strategic military access
It still exists. Still walkable. Still defiant.
Via Egnatia—East Meets West
Stretching from the Adriatic coast to Byzantium, this route linked Rome to the Greek world and later served the Byzantine and Ottoman empires.
Empires changed. The road stayed relevant.
Via Augusta—Rome’s Iberian Backbone
This route unified Roman Spain, supporting trade, administration, and cultural integration across the peninsula.
Maintenance: The Secret Ingredient Everyone Forgets
Roman roads didn’t last because they were built once. They lasted because they were maintained relentlessly.
- Dedicated road officials
- Regular inspections
- Local communities legally obligated to assist
Neglect was not an option. Infrastructure was policy.
The Psychology of Roman Roads
A Roman road was a message carved into the land.
Straight lines projected dominance. Milestones bearing imperial names reinforced loyalty. Travelers understood one thing clearly: Rome was present even when soldiers were not.
This psychological effect mattered. It reduced resistance. It normalized Roman authority. Roads made empire feel inevitable.
Archaeological Evidence: Proof, Not Poetry
Excavations across Europe and the Mediterranean reveal:
- Wheel ruts etched into stone
- Drainage systems still functional
- Road alignments matching satellite imagery
In some regions, modern GPS mapping shows highways following Roman routes within meters. That is not coincidence. That is inherited intelligence.
Cesta Roman and the Modern World
Infrastructure Legacy
Modern road design borrows heavily from Roman principles:
- Load-bearing foundations
- Straight routing for efficiency
- Integrated drainage
Rome did not invent asphalt, but it invented discipline.
Urban Planning
Cities grew along Roman roads. Many still do. London, Paris, Cologne, and Milan each owes its layout partly to Roman routing logic.
The past quietly directs traffic.
Common Misconceptions About Roman Roads
Roman roads are often misunderstood as crude stone paths built only for marching armies, but this oversimplification ignores their technical and strategic depth. While military efficiency drove their construction, these roads were equally designed for trade, governance, and civilian mobility. Another common misconception is that Roman roads were always perfectly straight; in reality, they balanced directness with terrain intelligence, adapting routes to geography, drainage, and long-term durability. Far from being rigid or uniform, Roman roads reflected a flexible engineering philosophy that prioritized function, resilience, and sustained use over visual symmetry or short-term speed.
Why Cesta Roman Still Matters
Cesta Roman still matters because it set the foundation for infrastructure built to endure, not merely to function. Designed for generations, these roads prioritized geography, durability, and efficiency over short-term convenience. Many modern routes still follow Roman paths, proving the precision of their planning. More than engineering, Cesta Roman shaped political stability, economic integration, and cultural exchange by reducing fragmentation and enabling reliable movement. It remains a lasting lesson that systems built with long-term vision can outlive empires and continue delivering value.
Conclusion
The Roman road system was far more than a network of ancient roads; it was the structural backbone of Roman civilization. Its precision, scale, and durability reveal a mindset that valued foresight over speed and permanence over improvisation. By enabling military control, economic integration, administrative efficiency, and cultural transmission, these roads transformed Rome from a regional power into a unified empire. Their continued presence in modern landscapes proves that intelligent design transcends time. Cesta Roman stands as enduring evidence that infrastructure, when built with clarity of purpose and technical discipline, becomes a civilizational force rather than a historical artifact.
FAQs
Q. What does Cesta Roman mean?
Cesta Roman refers to the Roman road system, engineered routes constructed by the Roman Empire to connect cities, provinces, and strategic locations.
Q. Why are Roman roads still visible today?
They were built using layered stone construction and advanced drainage methods, making them exceptionally durable compared to later road systems.
Q. Were Roman roads only used for military purposes?
No. While military movement was a priority, Roman roads also supported trade, administration, communication, and cultural exchange.
Q. Do modern roads follow Roman routes?
Yes. Many modern highways and urban layouts in Europe align closely with ancient Roman road paths due to their efficient geographic planning.
Q. What is the biggest lesson from Cesta Roman today?
The greatest lesson is that infrastructure designed with long-term vision and system-level thinking can outlast political power and remain useful for centuries.